Azure Policy allows us to control what actions users can perform regarding creating and managing resources in Azure. We can define policies for naming standards, require that certain extensions be installed on virtual machines, audit various resources for certain configurations… the possibilities are endless.
In this article, well focus on defining what locations users can deploy resources in. To get started, login to the Azure Portal and search for “Policy”.
Click on “Definitions”. Here you will find several built-in definitions that can be applied to your resources. Definitions are a json template containing the logic for what you want to accomplish. It is worth investing some time to look through these built-in definitions.
In the “search” field, type in “location”. Then, click on the “Allowed Locations” definition.
Here you can see the json content of the definition. The “policyRule” section is the bread and butter of the definition. In this particular example, the policyRule states that if the location that the user is deploying a resource to is NOT a) in the list of allowed locations, b) global, or c) a b2c directory, then deny the deployment.
Next, click on “Assign”.
You can assign the policy to a subscription or resource group. You can also create exclusions in this same window, and enable or disable the policy.
Click “Next”, and on the Parameters page, choose the allowed locations from the drop down menu. Then click next.
Azure Policy has the capability to remediate non-compliant resources. An example would be having a policy that requires anti-virus be installed on all servers. If Azure Policy detected a server that did NOT have anti-virus installed, it would use a managed identity to install AV software on the server. This particular policy does not need a remediation action, so we will just click “Next” here.
On the Review + Create window, review the resource and then click “Create”.
Back on the Azure Policy blade, select “Assignments”. We can now see that our new policy is assigned.
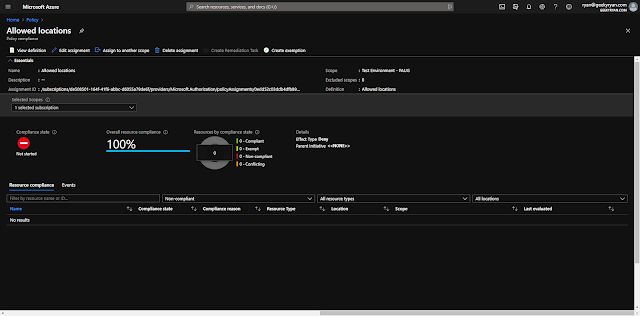
Back on the “Overview” page, you can track compliance for the policy. We can see here that compliance for the “Allowed Locations” policy assignment has not yet been started. This typically takes an hour or so before the compliance state is updated.
Click on the Policy to get a more detailed view of compliance, view the definition, edit the assignment, and even create exemptions.







No comments:
Post a Comment